|
 <#"700677.files/image021.gif">
<#"700677.files/image022.gif"> <#"700677.files/image023.gif"> <#"700677.files/image021.gif">
<#"700677.files/image022.gif"> <#"700677.files/image023.gif">
In addition
to this there are many types of convex quadrilaterals, such as a parallelogram,
rectangle, rhombus, square, trapezoid
<#"700677.files/image024.jpg">
A rectangle
<#"700677.files/image025.jpg">
rhombus
<#"700677.files/image026.jpg">
A square
<#"700677.files/image027.gif">
A trapezoid
<#"700677.files/image028.gif">
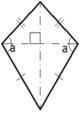
kite has two
pairs of sides. Each pair is made up of adjacent sides that are equal in
length. The angles are equal where the pairs meet. Diagonals (dashed lines)
meet at a right angle, and one of the diagonal bisects (cuts equally in half)
the other.
4. Circles
circle is a
simple shape <#"700677.files/image030.jpg"> from the
center <#"700677.files/image031.jpg"> is called
the center <#"700677.files/image032.jpg">. The angle
a circle subtends from its center is a full angle
<#"700677.files/image033.jpg"> or 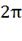 radians
<#"700677.files/image035.gif"> radians
<#"700677.files/image035.gif">
are two main
"slices" of a circle"pizza" slice is called a sector
<#"700677.files/image036.jpg">
this paper I have tried to introduce
several two-dimensional geometric figures and some of their properties. I
introduced triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, their classifying by different
bases, circle and its parts, which are used for solving practical
problems.school the course of geometry consist of two parts - plan geometry and
space geometry. In school courses plane geometry or two-dimensional geometric
figures are studied in 7th, 8th and 9th grade and they are the basis of
geometry. Space geometry or three-dimensional geometric shapes are studied in
10th, 11th and 12th grade, but during the study of three-dimensional geometric
shapes two-dimensional geometric figures are widely used. In addition to this
two-dimensional geometric figures are defined as parts of three-dimensional and
n-dimensional shapes. Our world is three- dimensional, that's why we must know
common properties of three-dimensional geometric shapes, therefore we must
recognize also two-dimensional geometric figures.dimensional geometric figures
are widely used in the practise, so everybody must know some properties of
geometric figures and their applications.geometry is very beautiful and
practice subject and it develops the student’s analytical and visual thinking,
which explains its essential role in our life.
Glossary
1. Point- points are
zero-dimensional <#"700677.files/image002.jpg">-gon- A polygon with  vertices
and vertices
and  sides is
known as an sides is
known as an  -gon -gon
7. Convex
<http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ConvexPolygon.html> polygon-A planar
polygon <http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Polygon.html> is convex if it
contains all the line segments
<http://mathworld.wolfram.com/LineSegment.html> connecting any pair of
its points
8. Concave
<http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ConcavePolygon.html> polygon-A concave
polygon is a polygon <http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Polygon.html> that is
not convex <http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ConvexPolygon.html>
. Triangle- A triangle is a
3-sided polygon <http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Polygon.html> sometimes
called the trigon
10. Triangle
geometry <http://mathworld.wolfram.com/TriangleGeometry.html>- The study
of triangles is sometimes known as triangle geometry
<http://mathworld.wolfram.com/TriangleGeometry.html>
11. Equilateral
triangle <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equilateral_triangle> - The
triangle where all sides have the same length
. Isosceles triangle-the
triangle where two sides are equal in length
. Scalene triangle- the
triangle where all sides and all angles are unequal
14. Right
triangle <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Right_triangle> or right-angle
triangle- the triangle that has a right interior angle
. Hypotenuse- The side
opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypotenuse>; it is the longest side of the
right triangle
. Legs- The other two sides
of right triangle are called the legs
. Oblique triangles-
Triangles that do not have an angle that measures 90°
18. Acute triangle or acute-angled
triangle.- A triangle that has all interior angles measuring less than 90°
19. Obtuse triangle or
obtuse-angled triangle- A triangle that has one interior angle that measures
more than 90°
20. Quadrilateral - A
quadrilateral is a polygon <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polygon> with
four sides (or edges) and four vertices or corners
21. Parallelogram
<http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/parallelogram.html>- a quadrilateral,
which opposite sides are parallel and equal in length
22. Rectangle
<http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/rectangle.html>- a quadrilateral,
which has four right angle <http://www.mathsisfun.com/rightangle.html>s
(90°). Also opposite sides are parallel
<http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/parallel-lines.html> and of equal
length.
23. Rhombus
<http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/rhombus.html>- A quadrilateral,where
all sides have equal length
25. Trapezoid
<http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/trapezoid.html>- a quadrilateral,
which has a pair of opposite sides parallel
. Kite- a quadrilateral,
which has two pair sides, Each pair is made up of adjacent sides that are equal
in length
. Circle-is two-dimensional
shapes that is the set of all points
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Point_(geometry)> in a plane
<http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plane_(mathematics)> that are a given
distance from a given point
. Center- A point inside the
circle. All points on the circle are equidistant (same distance) from the
center point
. Radius-The radius is the
distance from the center to any point on the circle. It is half the diameter.
. Diameter- The distance
across the circle. The length of any chord
<http://www.mathopenref.com/chord.html> passing through the center. It is twice
the radius
. Circumference- the
circumference is the distance around the circle
. Chord- A line segment
linking any two points on a circle
. Tangent- A line passing a
circle and touching it at just one point
. Secant- A line that
intersects a circle at two points
References
1. Լ.Ս.
Աթանասյան,
Վ.Ֆ.
Բուտուզով
<<Երկրաչափութուն
7>> Երևան
<<Զանգակ
97>> 2006թ.
2. Լ.Ս.
Աթանասյան,
Վ.Ֆ.
Բուտուզով
<<Երկրաչափութուն
8>> Երևան
<<Զանգակ
97>> 2007թ.
3. Լ.Ս.
Աթանասյան,
Վ.Ֆ.
Բուտուզով
<<Երկրաչափութուն
9>> Երևան
<<Զանգակ
97>> 2008թ.
4. <http://www.mathsisfun.com/>
Похожие работы на - Geometric figures
|